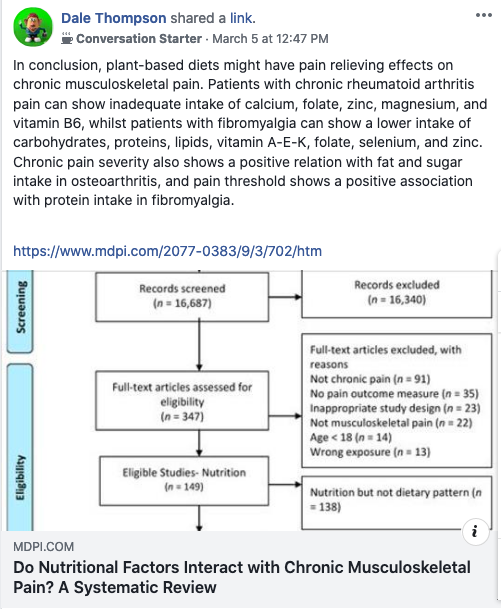
Do Nutritional Factors Interact with Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain? A Systematic Review On the basis of the available literature, there is some evidence that plant-based dietary patterns such as vegetarian and vegan diets might have pain-relieving effects on chronic musculoskeletal pain. This effect might arise from the anti-inflammatory characteristics of the plant-based dietary patterns, but studies exploring the mechanisms behind the pain-relieving effects of dietary interventions for patients with chronic musculoskeletal pain are needed. There is also inconclusive evidence that patients may show inadequate intake of calcium, folate, zinc, magnesium, and vitamin B6 in chronic rheumatoid arthritis pain and a lower intake of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, vitamin A-E-K, folate, selenium, and zinc in chronic fibromyalgia pain compared to the reference values and data of healthy people, respectively. Moreover, pain severity is positively associated with fat and sugar intake in chronic osteoarthritis pain, and pain threshold is positively associated with protein intake. However, the mechanisms behind this interaction are still uncertain, and more high-quality studies that investigate the underlying mechanisms of the interaction between chronic musculoskeletal pain and nutrition are needed.
#science #chiropractor #chiropractic #research #education #evidence based #patient centered #interprofessional #collaborative #rehabilitation #public health #spinal health #musculoskeletal health #ethics #pain #function #disability #QOL #knowledgetranslation


