Manual Therapy Reduces Pain Behavior and Oxidative Stress in a Murine Model of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type I
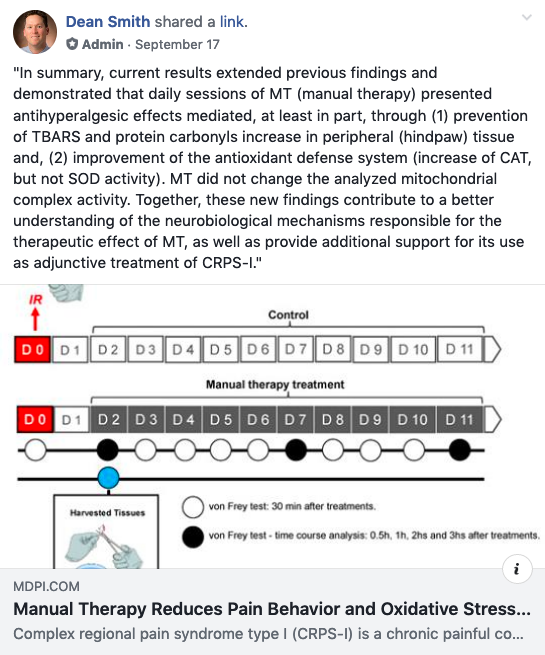
"In summary, current results extended previous findings and demonstrated that daily sessions of MT (manual therapy) presented antihyperalgesic effects mediated, at least in part, through (1) prevention of TBARS and protein carbonyls increase in peripheral (hindpaw) tissue and, (2) improvement of the antioxidant defense system (increase of CAT, but not SOD activity). MT did not change the analyzed mitochondrial complex activity. Together, these new findings contribute to a better understanding of the neurobiological mechanisms responsible for the therapeutic effect of MT, as well as provide additional support for its use as adjunctive treatment of CRPS-I."
#science #chiropractor #chiropractic #research #education #evidence based #patient centered #interprofessional #collaborative #rehabilitation #public health #spinal health #musculoskeletal health #ethics #pain #function #disability #QOL


