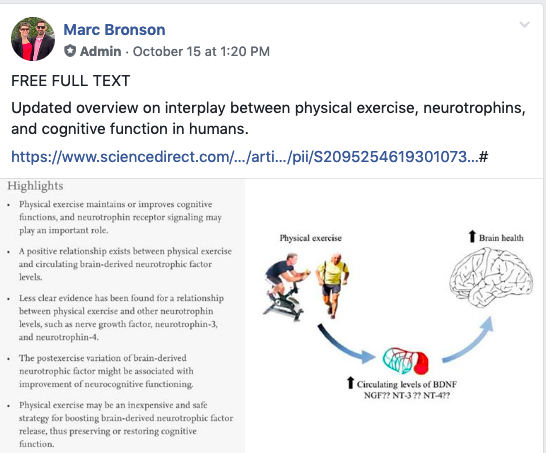
Physical exercise maintains or improves cognitive functions, and neurotrophin receptor signaling may play an important role.
•A positive relationship exists between physical exercise and circulating brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels.
•Less clear evidence has been found for a relationship between physical exercise and other neurotrophin levels, such as nerve growth factor, neurotrophin-3, and neurotrophin-4.
•The postexercise variation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor might be associated with improvement of neurocognitive functioning.
•Physical exercise may be an inexpensive and safe strategy for boosting brain-derived neurotrophic factor release, thus preserving or restoring cognitive function.
Updated overview on interplay between physical exercise, neurotrophins, and cognitive function in humans
#science #chiropractor #chiropractic #research #education #evidence based #patient centered #interprofessional #collaborative #rehabilitation #public health #spinal health #musculoskeletal health #ethics #pain #function #disability #QOL


